Check CPU Architecture
Make sure .dll files are correctly installed. A 64-bit operating system can run 32-bit applications without any issues. However, 32-bit operating systems are unable to run 64-bit applications.
- x86 (32-Bit): This architecture is also known as 32-bit and is mostly used on older systems. It can handle up to 4GB of memory.
- x64 (64-Bit): Also known as 64-bit, this architecture is used on most modern systems and can handle significantly larger amounts of memory than x86.
- ARM/64: This architecture type is used for devices that are powered by ARM processors, such as smartphones and tablets.
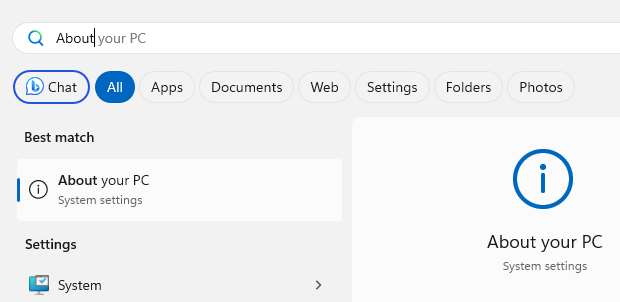
Click the 'Start' menu and enter 'About your PC'.
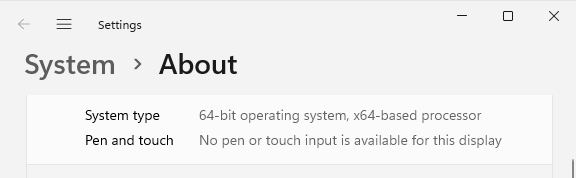
Either "32-bit" or "64-bit" will be displayed under the system type.
Did you know?
Some DLLs are "self-registering", meaning they update the Windows registry with their details when installed or first run. This ensures that applications can find and interface with them correctly.
